如何在 Python 中使用 Vultr 托管数据库进行缓存
介绍
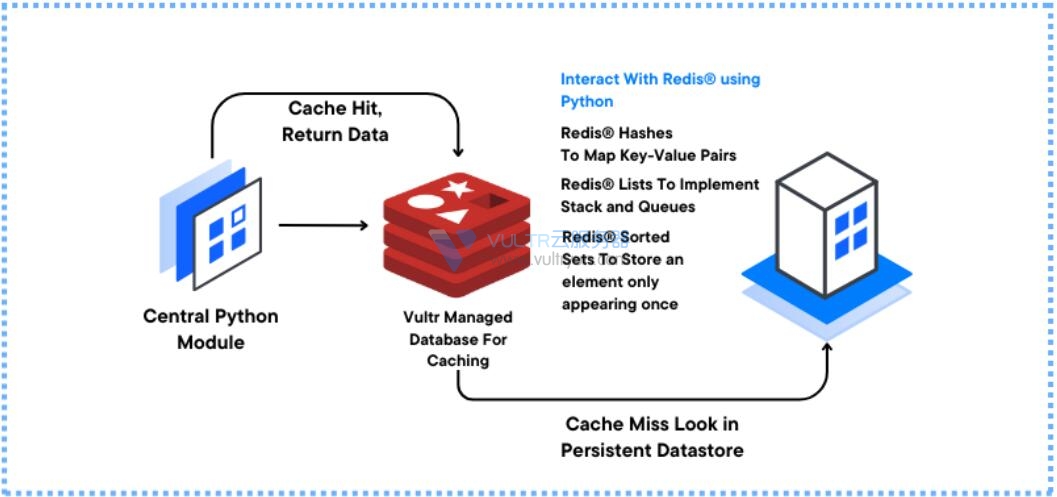
Redis® 是一种内存数据存储,提供灵活的数据结构、高性能和按需可扩展性。Vultr Managed Database for Caching 为任务关键型应用程序提供高可用性、高吞吐量和低延迟。本指南介绍如何在 Python 中使用 Vultr Managed Database for Caching 创建高可用性应用程序。
先决条件
准备工作:
- 购买用于缓存的 Vultr 托管数据库
- 购买 Vultr Linux 服务器以用作开发计算机
- 使用 SSH 以非 root 用户身份访问服务器
设置 Python 开发环境
要将 Vultr Managed Database for Caching 集成到 Python 应用程序,请安装 Python 模块并设置示例项目目录来存储应用程序文件。redis
- 升级 Python 包管理器。
pip$ pip install --upgrade pip - 安装 Python 驱动程序以连接到 Redis® 数据库。
redis$ pip install redis - 创建一个新目录。
project$ mkdir project - 导航到新目录。
project$ cd project
创建 Redis® 网关类
要在 Python 应用程序文件中使用 Vultr Managed Database for Caching 连接,请创建一个连接到数据库的中央 Python 模块。然后,可以通过在应用程序中使用子句声明数据库模块来重用该模块。按照以下步骤创建 Redis® 连接模块import
- 使用 Vim 等文本编辑器创建一个新文件
redis_gateway.py$ nano redis_gateway.py - 将以下代码添加到文件中。将 、 和 值替换为正确的 Vultr Managed Database for Caching 详细信息
vultr-prod-abcd.vultrdb.com16752example-passwordimport redis class RedisGateway: def __init__(self): r_host = 'vultr-prod-abcd.vultrdb.com' r_port = 16752 r_pass = 'example-password' self.r_client = redis.Redis( host = r_host, port = r_port, password = r_pass, ssl = 'true' )保存并关闭文件
上面的 Python 应用程序代码使用方法声明一个类。每次创建类的实例时,都会执行此方法。然后,它使用该函数连接到 Redis® 数据库。
RedisGateway__init__(self)RedisGatewayself.r_client = redis.Redis(...)要将 Redis® 数据库模块导入到其他 Python 源代码文件,请使用以下声明:
import redis_gateway r_gateway = redis_gateway.RedisGateway() r_client = r_gateway.r_client
实现 Redis® 字符串
在 Redis® 中,字符串是字节序列,是最常用的数据类型。您可以使用字符串数据类型来存储会话 ID、用户密码、产品信息和静态 HTML 内容。要在 Redis® 服务器中创建密钥,请使用关键字。若要检索键值,请使用关键字。在本节中,创建一个 Python 应用程序来实现 Redis® 字符串,如下所述。setget
- 创建新文件
redis_strings.py$ nano redis_strings.py - 将以下内容添加到文件中
import redis_gateway r_gateway = redis_gateway.RedisGateway() r_client = r_gateway.r_client r_key = "john_doe" r_value = "example-password" r_client.set(r_key, r_value) print("...\r\n You've successfully set the Redis key.\r\n") if r_client.exists(r_key): r_value = r_client.get(r_key).decode("utf-8") print("The value for the " + r_key + " key is " + r_value + "\r\n ...")Save and close the file.
The above application file imports the module you created earlier, then:
redis_gatewayr_key: Defines the name of the string key you're setting in the Redis® databaser_value: Defines the Redis® key valuer_client.set(r_key, r_value): Sets the key in the Redis® databaseif r_client.exists(r_key): Verifies whether the key exists in the Redis® database server before retrieving it to avoid run time errorsr_client.get(r_key).decode("utf-8"): Retrieves the key from the Redis® database
- Run the Redis® strings application file
$ python3 redis_strings.pyOutput:
... You've successfully set the Redis key. The value for the john_doe key is example-password ...As displayed in the above output, Python correctly connects to the Redis® database and sets the value for the string key .
example-passwordjohn_doe
Implement Redis® Lists
A Redis® list is an ordered collection of strings used to implement queueing mechanisms. Redis® allows you to add elements to the head or tail of a list using the and commands. Create a new Python application to test the Redis® Lists functionality as described below.lpushrpush
- Create a new file
redis_lists.py$ nano redis_lists.py - Add the following contents to the file
import redis_gateway import json r_gateway = redis_gateway.RedisGateway() r_client = r_gateway.r_client r_list = "sample_customer_job_list" sample_job_1 = { "firstName": "JOHN", "lastName": "DOE", "email": "john_doe@example.com" } sample_job_2 = { "firstName": "MARY", "lastName": "SMITH", "email": "mary_smith@example.com" } r_list_value_1 = json.dumps(sample_job_1) r_list_value_2 = json.dumps(sample_job_2) r_client.lpush(r_list, r_list_value_1, r_list_value_2) print("...\r\n You've successfully added a customer registration jobs to the Redis list.\r\n...") while(r_client.llen(r_list) != 0): print("The values for the " + r_list + "\r\n...") print(r_client.lpop(r_list).decode("utf-8") + "\r\n...")Save and close the file.
Below is what the above application code does:
- The variable represents the key of your sample Redis® list.
r_list sample_job_1 = {...}and are sample list values.sample_job_1 = {...}- The function inserts the two sample jobs into the Redis® list
r_client.lpush(r_list, r_list_value_1, r_list_value_2) - The loop queries the Redis® server and iterates through the variable to print the list values
while(r_client.llen(r_list) != 0):r_list
- The variable represents the key of your sample Redis® list.
- Run the application file
redis_lists.py$ python3 redis_lists.pyOutput:
... You've successfully added a customer registration jobs to the Redis list. ... The values for the sample_customer_job_list ... {"firstName": "MARY", "lastName": "SMITH", "email": "mary_smith@example.com"} ... The values for the sample_customer_job_list ... {"firstName": "JOHN", "lastName": "DOE", "email": "john_doe@example.com"} ...
Implement Redis® Hashes
Redis® hashes are record types that map keys to value pairs. Implement Redis® hashes in the form of company data in a Python application as described below.
- Create a new file
redis_hash.py$ nano redis_hash.py - Add the following contents to the file
import redis_gateway import json r_gateway = redis_gateway.RedisGateway() r_client = r_gateway.r_client r_hash = "company_profile" r_client.hset(r_hash, "company_name", "XYZ COMPANY") r_client.hset(r_hash, "add_line_1", "123 SAMPLE STREET") r_client.hset(r_hash, "add_line_2", "APT BUILDING") r_client.hset(r_hash, "county", "3RD COUNTY") r_client.hset(r_hash, "city", "SUN CITY") r_client.hset(r_hash, "zip", "123456") print("...\r\nYou've successfully set a company profile.\r\n...") print("Company profile information \r\n" ) print(json.dumps(str(r_client.hgetall(r_hash)))) print("Company Name : " + r_client.hget(r_hash, "company_name").decode("utf-8"))Save and close the file.
In the above application:
- The variable represents the hash key in the Redis® database.
r_hash - The function sets a hash in the Redis server. This function is the same as:
r_client.hset(r_hash, "company_name", "XYZ COMPANY")company_profile['company_name'] = "XYZ COMPANY" r_client.hgetall(r_hash): Retrieves all key-value pairs for a given hashr_client.hget(r_hash, "company_name"): Retrieves the value of a given key in the hash
- The variable represents the hash key in the Redis® database.
- Run the application
$ python3 redis_hash.pyOutput:
... You've successfully set a company profile. ... Company profile information "{b'company_name': b'XYZ COMPANY', b'add_line_1': b'123 SAMPLE STREET', b'add_line_2': b'APT BUILDING', b'county': b'3RD COUNTY', b'city': b'SUN CITY', b'zip': b'123456'}" Company Name : XYZ COMPANY
Implement Redis® Sorted Sets
Sorted sets represent a collection of strings arranged by an associated score. An element can only appear once in a sorted set. Redis® offers the and functions for adding and retrieving sorted sets values. Implement these functions in a Python application as described below.zaddzrange
- Create a new file
redis_sorted_set.py$ nano redis_sorted_set.py - Add the following contents to the file
import redis_gateway import json r_gateway = redis_gateway.RedisGateway() r_client = r_gateway.r_client r_sorted_set = "database_ratings" database_scores = { 'MySQL': 1, 'PostgreSQl': 2, 'SQLite': 3, 'MongoDB': 4 } r_client.zadd(r_sorted_set, database_scores) print("...\r\nYou've successfully entered four database ratings.\r\n...") print("Database rating information: \r\n") print(r_client.zrange(r_sorted_set, 0, 3))Save and close the file.
In the above application:
r_sorted_set: Declares a key for the sorted setdatabase_scores = {...}: Contains four elements with a matching scorer_client.zadd(r_sorted_set, database_scores): Adds the set elements to the Redis® serverr_client.zrange(r_sorted_set, 0, 3): Returns all sorted set values from the database
- Run the application
$ python3 redis_sorted_set.pyOutput:
... You've successfully entered four database ratings. ... Database rating information: [b'MySQL', b'PostgreSQl', b'SQLite', b'MongoDB']
结语
在本指南中,您已使用 Vultr Managed Database for Caching with Python 实现了不同的数据类型。根据您的应用程序用例,实现相关的 Redis® 数据类型以在数据库中缓存和存储数据。